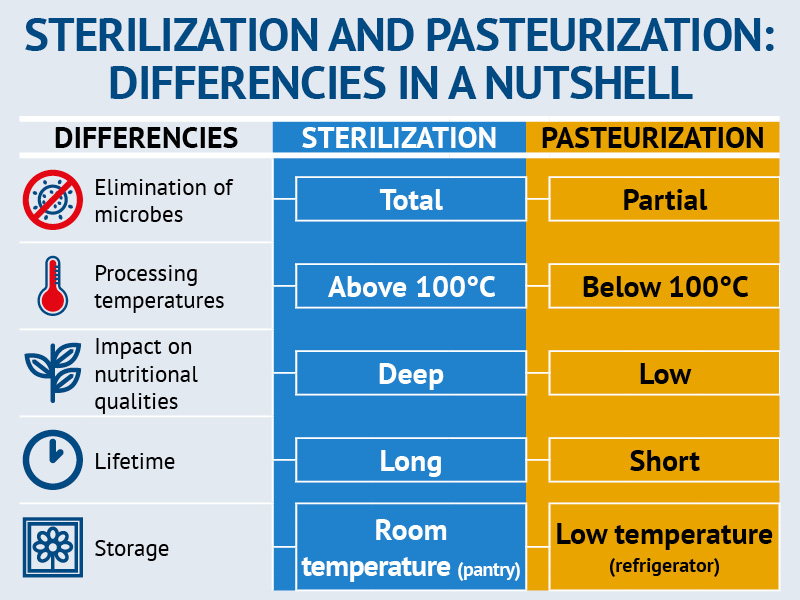
The process is intended to destroy or deactivate organisms and enzymes that contribute to spoilage or risk of disease including vegetative bacteria but not bacterial spores. The sterilization is a process that destroys all microorganisms and their spores while the pasteurization destroys.
At 65C you would need 35 minutes to accomplish a 5D reduction.
Pasteurization vs sterilization temperature. Sterilization is a temperature based preservation technique referring to any process that removes or destroys all forms of life and other biological agents mainly in food items. In contrast pasteurization is a temperature based preservation technique referring to any process that removes or destroys all forms of pathogenic microorganisms mainly in food items. The main difference between Pasteurization and Sterilization is that Pasteurization is the method of cooking food particularly liquids to heat at a particular temperature to stop the growth of microbes in the food whereas sterilization is the method of killing all the microbes and.
Sterilization can be both physical or chemical. Physical sterilization means sterilization with heat or even cold sterilization. Chemical sterilization means gas sterilization using chemical agents or cold sterilization.
Pasteurization depends on temperature and can be vat pasteurization HHST HTST. Sterilization vs Pasteurization Some of the microorganisms are useful and even necessary for everyday life. However there are a huge number of microorganisms that can cause disease or damage to useful resources.
Different methods are used in order to kill harmful microorganisms. The sterilization is a process that destroys all microorganisms and their spores while the pasteurization destroys. Pasteurization vs Sterilization.
Pasteurization CFIA The processes is normally developed by a process authority. The target organism depends on the product storage temperature and safety parameters. Targeting non-proteolytic Clostridium botulinum will control both spore and non-spore formers in a refrigerated product.
Monocytogenes prevents the growth of other non-spore formers. Whereas the sterilization process heats food to 120C248F pasteurization is achieved in the 70-90C range explains Tang a professor of food engineering at the Pullman Wash school. System design is different than for sterilization he adds with no need for pressurization and it has been shown to be effective against both pathogens such as Listeria and Clostridium botulinum and the human norovirus.
Specific temperatures must be obtained to ensure the microbicidal activity. The two common steam-sterilizing temperatures are 121C 250F and 132C 270F. These temperatures and other high temperatures 830 must be maintained for a minimal time to kill microorganisms.
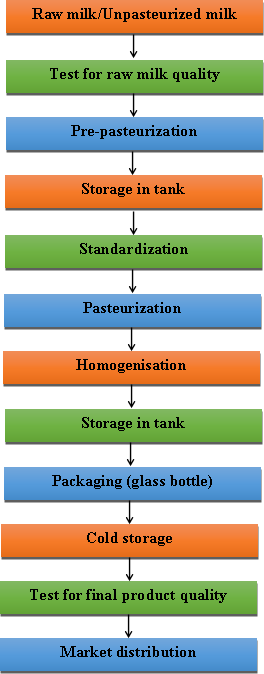
Recognized minimum exposure periods for sterilization of wrapped healthcare supplies are 30 minutes at 121C 250F in a gravity displacement sterilizer or 4 minutes at 132C 270F in a prevacuum sterilizer. A minimum time-temperature combination for the pasteurisation of milk. 628oC 145oF for 30 minutes now known as the batch or holder method.
This heat treatment was slightly above what many people at the time considered to be adequate exposure for the destruction of. By subjecting product to temperatures in excess of 100C and then packaging it in airtight containers. The basis of UHT is sterilization of the product before packaging then packaging it in pre-sterilized containers in a sterile atmosphere.
Processing dairy products in this manner using temperatures exceeding 135C. During moist heat sterilization the temperatures that are used vary from 110 to 130 degrees Celsius. Moist heat sterilization takes between 20 and 40 minutes the time being shorter the higher the temperature.
The use of dry heat sterilization uses longer times of susceptibility that may last up to 2 hours and that use much higher temperatures compared to moist heat sterilization. These temperatures may range from 160 to 180. 63C 145F 30 minutes.
72C 161F 15 seconds. 89C 191F 10 second. 90C 194F 05 seconds.
94C 201F 01 seconds. 96C 204F 005 seconds. 100C 212F 001 seconds.
If the fat content of the milk product is 10 percent 10 or more or if it contains added sweeteners the specified temperature shall be increased by 3. Pasteurized means that the milk has been heated to a minimum of 161F for a minimum of 15 seconds or 145F for 30 minutes for equivalent kill of bacteria and packaged under clean and sanitized conditions. Some bacteria survive pasteurization most often in very low numbers.
Pasteurization vs sterilization When moderately nutritious bulk substrates are pasteurized at 140-175F 60-80C some beneficial micro organisms mainly bacteria stay alive inhabit the substrate and guard it against other more aggressive micro organisms. Pasteurization or pasteurisation is a process in which packaged and non-packaged foods are treated with mild heat usually to less than 100 C to eliminate pathogens and extend shelf life. The process is intended to destroy or deactivate organisms and enzymes that contribute to spoilage or risk of disease including vegetative bacteria but not bacterial spores.
Since pasteurization is not sterilization and does not kill. Pasteurization is a low-temperature sterilization method invented in 1865 by a French named Pasteur. Pasteurized milk is sterilized by heating at 72-85C for 10-15 seconds.
Milk is heated by ultra-high temperature of 135-145C and kept for 2-4 seconds for sterilization. High temperature denatures the immunologically active protein in milk. 69ºC 155ºF 30 minutes.
80ºC 175ºF 25 seconds. High temperature short time Pasteurization HTST 83ºC 180ºF 15 seconds. High temperature short time Pasteurization HTST.
The efficacy of high-temperature short-time HTST pasteurization 72 degrees C15 s when low numbers or 103 cfu ml-1 of Mycobacterium paratuberculosis are present in milk was investigated. Raw cows milk spiked with Myco. Paratuberculosis 103 cfu ml-1 102 cfu ml-1 10 cfu ml-1 and 10 cfu 50 ml-1 was subjected to HTST pasteurization using laboratory pasteurizing units.
At 79C the D value has been reduced by two log cycles from that at 65C since the Z value is 7C. Hence it is now 007 min. The milk is processed for 2160035 min so that would accomplish 5 log cycle reductions to 4 organismsmL.
At 65C you would need 35 minutes to accomplish a 5D reduction.